Quantifying language changes surrounding mental health on Twitter
A. M. Stupinski, T. Alshaabi, M. V. Arnold, J. L. Adams, J. R. Minot, M. Price, P. S. Dodds, and C. M. Danforth
Times cited: 0
Abstract:
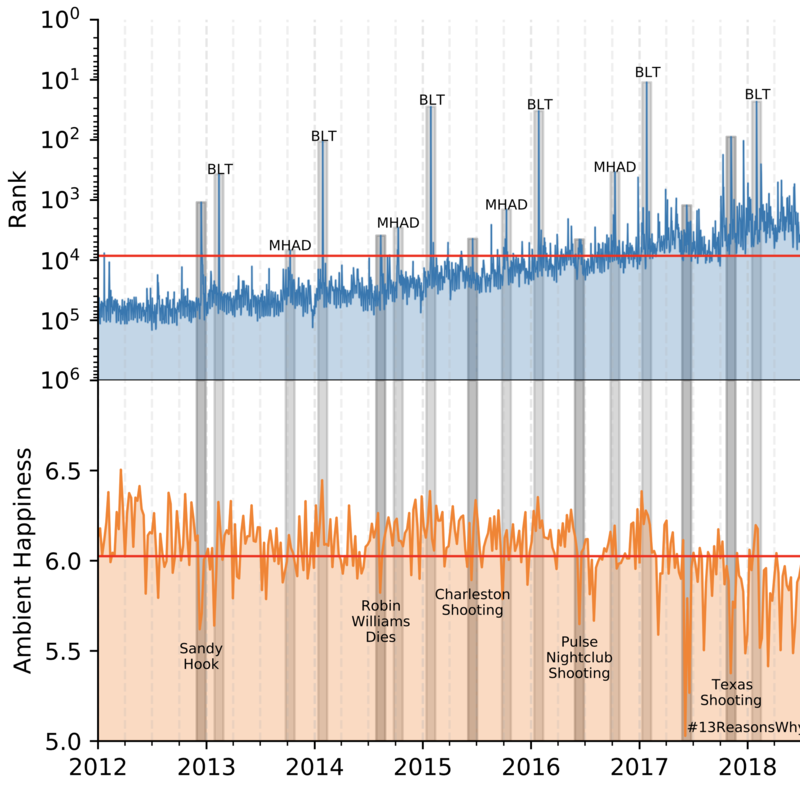
Mental health challenges are thought to afflict around 10\% of the global population each year, with many going untreated due to stigma and limited access to services. Here, we explore trends in words and phrases related to mental health through a collection of 1- , 2-, and 3-grams parsed from a data stream of roughly 10\% of all English tweets since 2012. We examine temporal dynamics of mental health language, finding that the popularity of the phrase 'mental health' increased by nearly two orders of magnitude between 2012 and 2018. We observe that mentions of 'mental health' spike annually and reliably due to mental health awareness campaigns, as well as unpredictably in response to mass shootings, celebrities dying by suicide, and popular fictional stories portraying suicide. We find that the level of positivity of messages containing 'mental health', while stable through the growth period, has declined recently. Finally, we use the ratio of original tweets to retweets to quantify the fraction of appearances of mental health language due to social amplification. Since 2015, mentions of mental health have become increasingly due to retweets, suggesting that stigma associated with discussion of mental health on Twitter has diminished with time.
- This is the default HTML.
- You can replace it with your own.
- Include your own code without the HTML, Head, or Body tags.
BibTeX:
@Misc{stupinski2021a,
author = {Stupinski, Anne Marie and Alshaabi, Thayer and
Arnold, Michael V. and Adams, Jane Lydia and Minot,
Joshua R. and Price, Matthew and Dodds, Peter
Sheridan and Danforth, Christopher M.},
title = {Quantifying language changes surrounding mental health on Twitter},
year = {2021},
note = {Available online at \href{https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01481}{https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01481}},
}